What Is Renewable Energy?
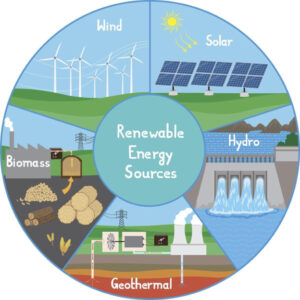
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continuously replenished, such as sunlight, wind, water flows, and biological materials. Unlike fossil fuels (oil, gas, coal), renewables do not run out and produce much lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Main Types of Renewable Energy
1️⃣ Solar Energy
Converts sunlight into electricity (solar PV) or heat (solar thermal).
✔ Low operating cost
✔ Scalable — from rooftops to utility-scale plants
2️⃣ Wind Energy
Wind turbines turn kinetic energy of the wind into electricity.
✔ One of the cheapest renewable sources
✔ Suitable for onshore and offshore installations
3️⃣ Hydropower
Uses flowing water (rivers, dams) to produce electricity.
✔ Stable and reliable
✔ Often used for baseload power
4️⃣ Biomass Energy
Organic materials (wood, agricultural waste, biogas) are burned or processed to produce heat, electricity, or biofuels.
✔ Useful for waste management
✔ Can provide continuous power
5️⃣ Geothermal Energy
Uses heat from beneath the Earth’s surface for electricity or direct heating.
✔ Very reliable
✔ Low emissions
💚 Why Renewable Energy Matters
- Reduces CO₂ emissions
- Enhances energy security
- Decreases dependence on imported fossil fuels
- Creates new jobs and industries
Provides long-term cost stability

HOW DOES SOLAR ENERGY WORK?
Below is a technical yet clear explanation of how a solar energy plant (solar PV power plant) works, including equipment, system philosophy, and energy flow.

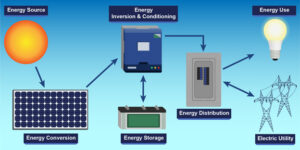
1. Technical Working Principle of a Solar Energy Plant (PV Plant)
A Solar PV Plant converts sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) modules. The produced electricity is DC (Direct Current), which is transformed into AC (Alternating Current) and injected into the electrical grid.
Step-by-Step Working Process
- Sunlight hits the PV modules
- Each module contains silicon cells.
- Photons strike the cell → electrons move → DC electricity is generated.
- DC power flows to string/combiner boxes
- Multiple modules are connected in series to form a string.
- Several strings connect in a combiner box which includes fuses & surge protection.
- DC power goes to the inverter
- The inverter converts DC ➝ AC, synchronizes with grid frequency (50 Hz), controls power quality, and maximizes energy via MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking).
- AC output goes to plant transformer
- Inverter output (typically 400–800 V AC) is stepped up by a Medium Voltage (MV) transformer to 11 kV / 20 kV / 33 kV.
- Power feeds the MV switchgear & protection system
- Circuit breakers, relays, isolators ensure protection & safety.
- Main transformer steps up MV ➝ HV
- For large utility plants, a final transformer increases voltage to transmission levels (e.g., 110–154–220 kV).
- Electricity is exported to the grid
- Plant SCADA monitors real-time production, faults, and conditions.
2. Major Equipment of a Solar PV Power Plant
A. Solar Field Equipment
- PV Modules
- Type: Mono-crystalline, Poly-crystalline, Bifacial
- Typical efficiency: 18–22%
- Mounted on fixed or tracking structures.
- Mounting Structures
- Fixed-tilt steel/aluminum structures.
- Single-axis trackers follow the sun east–west, increasing energy 15–25%.
- DC Cables & Connectors
- UV-resistant solar DC cables (4–6–10 mm²).
- MC4 connectors.
- String/Combiner Boxes
- Fuse protection for each string
- DC SPD (Surge Protection Device)
- DC isolator switch
- Monitoring (optional)
B. Power Conversion System
- Inverters
- Types:
✔ String Inverters (50–250 kW each)
✔ Central Inverters (1–5 MW each) - Functions:
- DC/AC conversion
- MPPT tracking
- Grid synchronization
- Harmonic filtering
- AC Distribution Panels
- AC SPD
- AC breaker
- Inverter output isolation
C. Transmission & Grid Interface
- MV/LV Transformers
- Step-up transformers (0.4 kV → 11/20/33 kV).
- Oil-filled or dry-type.
- MV Switchgear & Protection
- Circuit breakers (VCB/ACB)
- Current transformers (CT), voltage transformers (VT)
- Relays: Overcurrent, earth fault, differential protection.
- Main Step-Up Transformer (for grid)
- Converts MV → HV (e.g., 33 kV → 110/154/220 kV).
- Connects plant to transmission lines.
- Transmission Line
- Overhead line or underground cable to grid substation.
D. Monitoring, Control & Auxiliary Systems
- SCADA System
- Real-time monitoring of:
- Energy production
- Inverter performance
- String currents
- Transformer temperature
- Weather data
- Weather Monitoring Station (Meteo Station)
- Pyranometer (measures solar radiation)
- Temperature sensors
- Wind speed/direction sensors
- Earthing & Lightning Protection
- Grounding grid
- Lightning rods
- SPD in DC/AC panels
- Auxiliary Power Supply
- UPS + batteries
- Auxiliary transformer for internal loads
3. Philosophy of Operation of a Solar PV Plant
A. Energy Philosophy
- Convert maximum sunlight into electrical energy efficiently.
- Operate near the Maximum Power Point (MPP) of modules.
- Minimize losses in:
- Shading
- Soiling
- Wiring & inversion
- Transformer & transmission
B. Grid Philosophy
- Plant must deliver stable, high-quality AC power:
- Correct voltage
- Frequency 50 Hz
- Low harmonics
- Reactive power control (cos φ support)
C. Safety Philosophy
- Protection coordination between DC & AC sides
- Anti-islanding: plant disconnects automatically if grid fails
- Fire & arc protection
- Ground fault detection
D. O&M Philosophy (Operation & Maintenance)
- Preventive & predictive maintenance
- Regular panel cleaning
- Thermal imaging for hot-spot detection
- Inverter performance tracking
- String-level monitoring for faults
4. Simple Technical Flow Diagram (Text Version)
Sunlight → PV Modules → DC Strings → Combiner Box → Inverter → AC Output → MV Transformer → MV Switchgear → Main Transformer → Grid


