What is the best definition of environment?
Environment can be defined as a sum total of all the living and non-living elements and their effects that influence human life. While all living or biotic elements are animals, plants, forests, fisheries, and birds, non-living or abiotic elements include water, land, sunlight, rocks, and air
Why enviromet is important?
Our forests, rivers, oceans and soils provide us with the food we eat, the air we breathe, the water we irrigate our crops with. We also rely on them for numerous other goods and services we depend on for our health, happiness and prosperity. These natural assets are often called the world’s ‘natural capital’.
How can we protect the enviroment?
Protecting the environment means taking actions—big and small—that reduce harm to our planet’s air, water, land, and ecosystems. Here are the main ways we can do that, divided into practical categories:
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
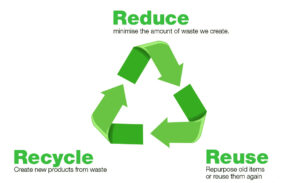
- Reduce: Buy only what you need. Choose products with less packaging.
- Reuse: Repair or repurpose items instead of throwing them away.
- Recycle: Separate waste properly (paper, plastic, glass, metal) and use local recycling programs.
- Save Energy

- Turn off lights, electronics, and chargers when not in use.
- Use energy-efficient appliances and LED bulbs.
- Insulate buildings to reduce heating and cooling needs.
Switch to renewable energy sources like solar or wind if possible.
- Use Sustainable Transportation
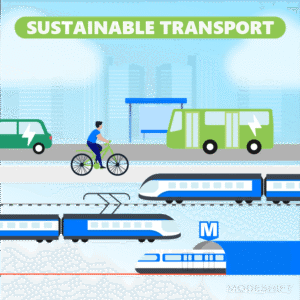
- Walk, cycle, or use public transportation when you can.
- Carpool or share rides to cut emissions.
- Choose electric or hybrid vehicles if possible.
- Conserve Water

- Fix leaks and use water-efficient fixtures.
- Turn off taps while brushing teeth or washing dishes.
- Reuse greywater for plants if local regulations allow.
- Protect Nature and Wildlife

- Plant trees and support reforestation.
- Avoid products that cause deforestation (like unsustainable palm oil).
- Support wildlife protection and avoid single-use plastics that harm animals.
- Support Clean Industry and Innovation

- Encourage companies to adopt cleaner technologies.
- Support circular economy practices—using waste as input for new products.
- Choose eco-friendly brands and sustainable products.
At this stage we want to study this subject from industrial points of view and introduce the ways of enviroment protection in industries that are or can be one of the most harmful phonemenon.
The indusrties mostly harm waters, soils and air. Now a days there are several ways to protect the enviroments from these harms of the industries . But we want to focus on the air polution in industries.
The air polution by industries are in 2 main categories. Dusts and chemical gas or mixtures of them. For poluting these harmful phenomonen there are different types of filters that are installed in the plants which can reduce(not compeltly eliminate) the dangers of them.
Below you will find a brief explanation of each and their applications.
air and gas filters are essential for protecting equipment, people, and the environment by removing dust, particulates, and contaminants from air or process gases.
Here’s a clear and complete overview of the main types of air and gas filters, categorized by function and application:
- Mechanical Filters

These remove solid particles (dust, pollen, fibers, etc.) from air or gas streams using physical barriers.
🔹 Types:
- Pre-filters / Coarse Filters:
Capture large dust and debris. Often the first filtration stage (e.g., G2–G4 in EN 779 or ISO coarse filters).
→ Used in HVAC systems, compressors, and air intakes. - Fine Filters / Secondary Filters:
Capture smaller particles like fine dust and spores (e.g., M5–M6 or ISO ePM10).
→ Used after pre-filters for better air quality. - HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) Filters:
Remove 99.97% of particles ≥0.3 µm.
→ Used in hospitals, cleanrooms, and pharmaceutical or electronic industries. - ULPA (Ultra-Low Penetration Air) Filters:
Even higher efficiency (≥99.999% for particles ≥0.12 µm).
→ Used in semiconductor or nuclear applications.
- Chemical / Gas-Phase Filters

Designed to remove gaseous pollutants like VOCs, SO₂, NOₓ, and odors.
🔹 Types:
- Activated Carbon Filters:
Adsorb organic gases and odors via carbon granules or impregnated carbon.
→ Used in air purification, chemical plants, and gas treatment. - Impregnated Alumina / Potassium Permanganate Filters:
Oxidize or neutralize acidic and basic gases.
→ Used in laboratories, refineries, and data centers. - Catalytic Filters:
Use catalysts to convert harmful gases (e.g., CO → CO₂).
→ Used in engine exhausts and industrial gas cleaning.
- Electrostatic Filters
Use electrical charges to capture particles.
🔹 Types:
- Electrostatic Precipitators (ESP):
Charge and collect dust particles on plates.
→ Used in power plants, cement kilns, and steel industries. - Electronic Air Cleaners:
Smaller versions for HVAC or air purifiers.
→ Used in buildings and clean environments.
- Bag Filters / Cartridge Filters
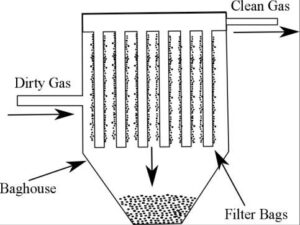
Capture dust and particulates from industrial process gases.
🔹 Types:
- Bag Filters (Bag House Filters):
Dust-laden gas passes through fabric bags; particles remain on the surface.
→ Used in cement, steel, and chemical industries.
(Common materials: polyester, PPS, Nomex, PTFE, fiberglass.) - Cartridge Filters:
Compact cylindrical filters made of pleated material for higher surface area.
→ Used in gas turbines, compressors, and dust collectors.
- HEAT-Resistant / High-Temperature Filters
Operate at elevated temperatures (up to 400–600°C).
🔹 Examples:
- Ceramic Filters: For hot gas filtration in incinerators and kilns.
- Metal Mesh Filters: For gas turbines and process gas protection.
- Coalescing Filters
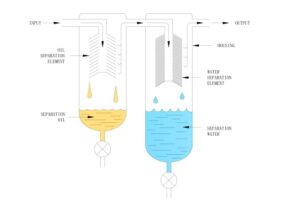
Separate liquids (oil, water droplets) from compressed air or gas.
→ Used in air compressors, pneumatic systems, and natural gas processing.
- HEPA + Activated Carbon Combination Filters

Hybrid filters combining particle and gas filtration, common in HVAC or clean air systems.
- Molecular Sieves & Membrane Filters
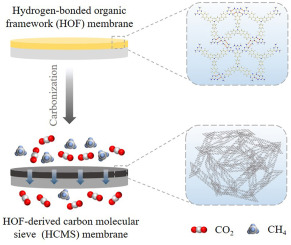
Used for gas purification and separation at the molecular level.
→ Used in oxygen/nitrogen generation, natural gas dehydration, and hydrogen purification.
Industry Examples
| Industry | Common Filter Types |
|---|---|
| Cement | Bag filters, ESP, cartridge filters |
| Chemical / Petrochemical | Activated carbon, coalescing, cartridge |
| Power plants | ESP, HEPA, SCR catalysts |
| HVAC / Cleanrooms | Pre, fine, HEPA, ULPA |
| Food & Pharma | HEPA, activated carbon, sterile air filters |
| Gas processing | Coalescing, molecular sieve, membrane |

