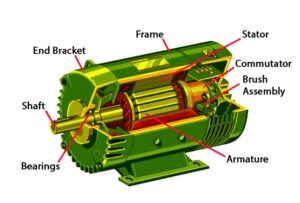
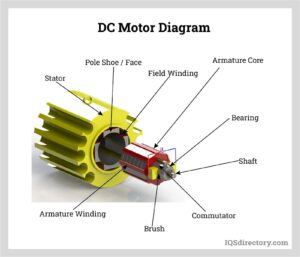
We know there are generally two types of motors, AC motor, and DC motor. AC motors are flexible for speed control and demand low power during start. On the other hand, DC motors are widely used due to its initial cost of low power units is less compared to AC and can be easily installed.
An AC motor can be defined as an electric motor that is driven by an alternating current (AC). A DC motor is also a rotatory electric motor that converts Direct current (DC energy) into mechanical energy. AC motors are mainly of two types – synchronous AC motors and induction motors.
A three-phase motor is an electric motor that typically receives its power from a three-phase system (three-phase current) This can be realised via a three-phase mains supply or a frequency inverter. Three-phase motors are available as synchronous and asynchronous motors.
In terms of application, AC power is more suitable for larger power generation and distribution, making it the source of electricity for outlets in homes and buildings. On the other hand, DC power has a smaller range of use cases, focusing more on low voltage and low current applications like electronic devices.
Understanding voltage classification is essential for the proper application and safety of electrical systems. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage.
According to American National Standard Institute(ANSI), high voltage transformers can handle a minimum of 115,000 to a maximum of 1,100,000 volts; medium voltage transformers has a limited capacity of 2400 to 69000 volts; and low voltage transformers have a minimum capacity of 240 volts and a maximum of 600 volts.